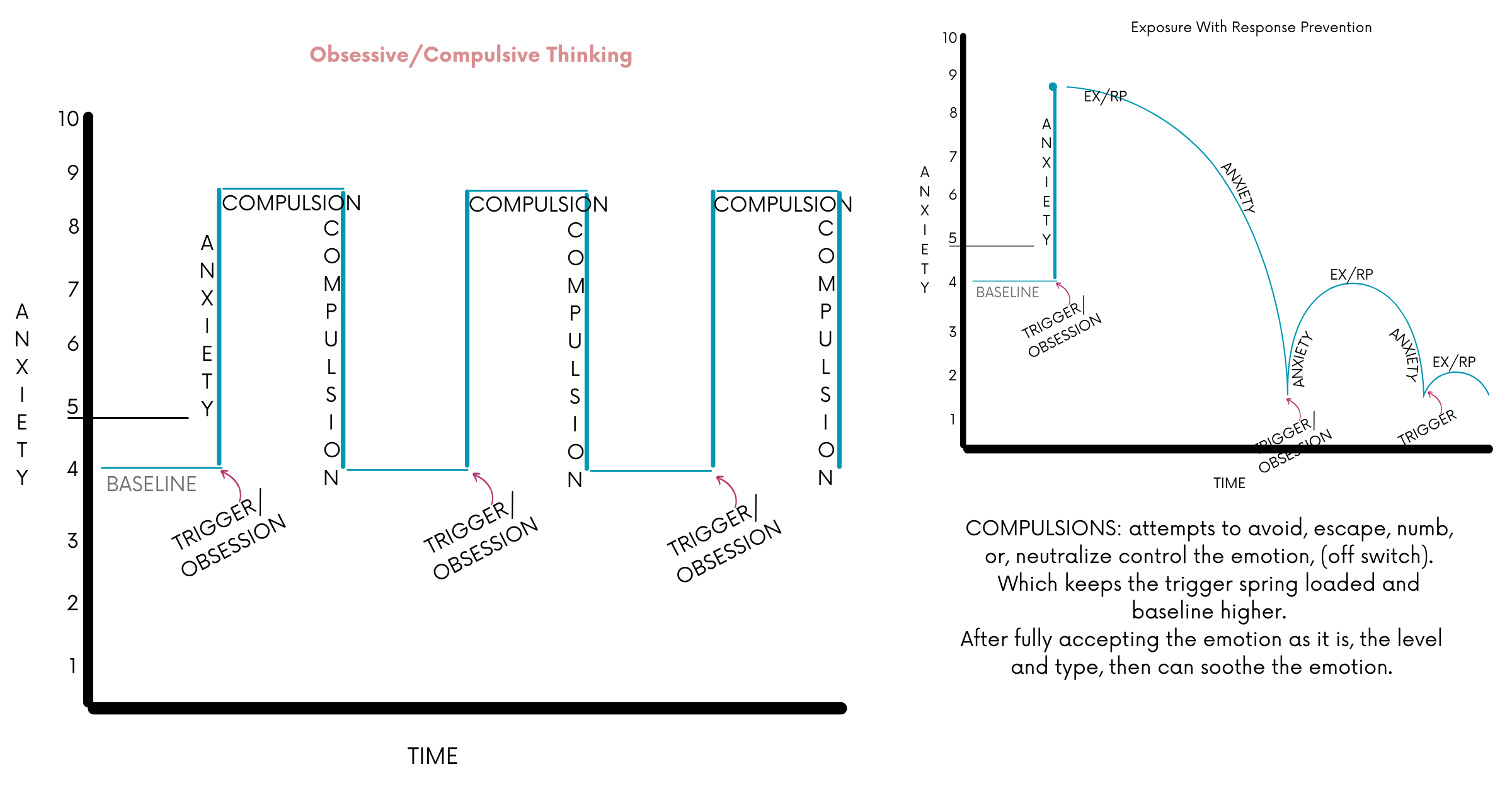
These visual diagrams are used as clinical tools during therapy sessions. Explanations and application are provided in-session, tailored to each client.
We can adjust & prevent
We can change
We can soothe
We can change
| Category | Signs & Behaviors | Examples | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional Avoidance |
|
|
|
| Emotional Expression |
|
|
|
| Emotional Processing |
|
|
|
Identifying Narcissistic Negging
| Negging Type | Example Phrases | Body Language | Common Situations | Intended Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backhanded Compliments | "You're pretty smart for someone who doesn’t have a degree." | Smirking, raised eyebrow, quick glance to see reaction | Casual conversations or group settings | Lowers self-esteem while appearing friendly |
| Comparisons & False Praise | "You’re actually not bad at this—better than I expected!" | Shrugging, dismissive tone, patronizing smile | After you achieve something or share good news | Undermines confidence, keeps you seeking approval |
| Diminishing Achievements | "That’s cute. I remember when I did something similar, but bigger." | Eye-rolling, exaggerated sighs, talking over you | After you share a success or skill | Makes you feel small, keeps attention on them |
| Disguised Insults | "You’d look great if you lost a little weight." | Side-eye, fake concern, touching your arm as if comforting | Discussing appearance, abilities, or choices | Creates insecurity while pretending to be helpful |
| Subtle Exclusion | "Oh, I didn’t think you’d be interested in this kind of thing." | Leaning away, whispering to others, avoiding eye contact | Social events, group activities, or work discussions | Makes you feel like an outsider, forces you to prove yourself |
| Fake Concern | "Are you okay? You seem really emotional lately." | Tilting head, faking concern, condescending tone | When you react to their negativity | Gaslights you into questioning your feelings |
| Shifting the Spotlight | "That’s nothing, let me tell you about the time I..." | Talking over you, dismissive hand gestures | Anytime you share an accomplishment or personal story | Keeps focus on them, devalues your experiences |
| Behavior | Tone & Body Language | Subtle Impact on You | Check-In: What's Really Happening? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lingers in your decision-making process | Slow, drawn-out comments; hesitant or knowing looks; stays engaged even after you've moved on | Makes you feel like you need their approval or input before finalizing your choice | Did you ask for their input, or are they offering it unsolicited? |
| Undermines or implies others won’t like your choice | “I mean, if that’s what you want…” (downward tone); exaggerated surprise; skeptical expressions; lowering voice as if sharing a secret | Creates doubt, makes you question if your decision is good enough or socially acceptable | Does their input feel genuinely helpful, or does it make you second-guess yourself? |
| Inserts themselves into your thoughts or decisions without adding helpful direction | “Well, I would’ve done it differently” or “I don’t know, I just don’t see it…” (dismissive tone); arms crossed or a knowing smirk | Makes you feel like they have some authority over your choices without providing actual value | Are they adding useful information, or just inserting themselves into your thought process? |
| Takes on a role of ‘advisor’ even when it’s not their place | Uses phrases like “You should…” or “I would never…” with a confident, leading tone; sighing or looking exasperated when you don’t agree | Shifts the dynamic so they are the expert and you are the one who needs guidance | Is it appropriate for them to advise you on this, or are they overstepping their role? |
| Acts like they ‘know better’ even when they don’t have relevant experience | “Trust me, I’ve been around long enough to know…” (said with an air of authority); tilting head with a slight smirk | Pressures you into following their perspective rather than making your own informed choice | Are they speaking from real knowledge, or just asserting influence? |
| Oversteps relational boundaries under the guise of ‘helping’ | Offers solutions that require them to be involved rather than providing neutral advice; subtly implies that you “need” them | Creates a sense of obligation to include them in your decisions | Is this person in a role where it makes sense for them to help, or are they inserting themselves where they don’t belong? |
1) Saw, heard, smelled
2) Thoughts: What I was saying to myself
3) Emotions: Sad, Fearful, Angry
It all started when….this was happening…(continue to describe what you experienced, including 1,2,3)……
Definition of antagonism within the DSM-5.
Antagonism (versus agreeableness): Behaviors that put the individual at odds with other people,
Including an exaggerated sense of self and concomitant (naturally accompanying),
Expectation of special treatment as well as a callous antipathy towards others,
Unawareness of others’ needs and feelings
And a readiness to use others in the service of self-enhancement.
The body language of someone with an exaggerated sense of self, expecting special treatment, showing callousness towards others, and using others for self-enhancement may exhibit the following non-verbal cues:
1. Exaggerated Sense of Self
Posture: Upright, rigid posture, often standing or sitting in a dominant position. They may position themselves in the center of a room or conversation, taking up more space than necessary.
Chin Tilted Up: This can suggest arrogance or superiority, with their chin slightly raised, making them appear to "look down" on others.
Grand Gestures: Large, sweeping hand movements to draw attention to themselves, often trying to dominate the space visually.
2. Expectation of Special Treatment
Impatient Movements: Tapping feet, checking their watch or phone, and sighing heavily when they feel they are not being prioritized. This behavior implies they believe they deserve immediate attention.
Ignoring Others: They may turn their body away from those they deem unimportant or not useful to them, signaling disinterest or disregard.
Eye-Rolling: Dismissive or disrespectful gestures, like rolling their eyes when they are not getting the attention they believe they deserve, can be common.
3. Callous Antipathy Towards Others
Cold or Blank Facial Expressions: They might maintain a neutral or disinterested face, showing little warmth or empathy toward others' emotions or concerns. No effort to mirror others' feelings.
Invading Personal Space: Stepping too close to others, not respecting personal boundaries, signaling dominance or disregard for others' comfort.
Interrupting Conversations: Cutting others off mid-sentence, often redirecting the conversation back to themselves, showing little care for others' input or needs.
4. Unawareness of Others’ Needs and Feelings
Lack of Eye Contact (with those considered 'beneath' them): They may avoid making direct eye contact with people they deem insignificant, showing little interest in engaging or connecting with others.
Self-Centered Gestures: Constantly adjusting their own appearance (fixing hair, straightening clothes) while others are speaking, signaling disinterest in what others have to say.
Talking Over Others: Raising their voice or dominating conversations without noticing or caring if others are uncomfortable or disengaged.
5. Readiness to Use Others for Self-Enhancement
Mirroring Behavior Selectively: They may mirror the body language of those they want to impress or extract something from, creating a false sense of connection to manipulate.
Feigning Interest (but only superficially): They may lean forward or make strong eye contact with people they are trying to impress or gain something from, but the interest is short-lived once their goal is achieved.
Dismissive Gestures: Turning away, crossing arms, or showing disinterest the moment they no longer find someone useful.
In essence, the body language reflects entitlement, dominance, and a lack of empathy. This person may seem commanding and confident, but their gestures reveal a lack of true connection with others, highlighting their self-serving motivations.
| Degree of Emotional Responsibility | Description | Examples | Should I Feel Their Feelings? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Emotional Harm (Highest Responsibility) | When you actively cause emotional harm, whether intentional or unintentional, you need to take full accountability and feel the emotional weight of your actions to understand the impact. | Saying something hurtful to someone in anger, intentionally mocking someone, or making a cruel joke at their expense. | Yes – You should feel their feelings because your actions have directly caused them harm, and empathy is essential for healing. |
| Neglect or Abandonment (Very High Responsibility) | Failing to act when someone relies on you, especially when it leads to feelings of being ignored or unwanted. | Not following through on a commitment, canceling plans last minute, or ignoring someone's emotional needs during a difficult time. | Yes – You should feel their feelings because your neglect or absence contributes to their emotional pain, and acknowledging that helps you repair the situation. |
| Deception for Personal Gain (High Responsibility) | When you deceive someone for personal gain or to maintain a facade, it can create significant emotional harm that you should be aware of and feel. | Lying to someone for personal benefit or manipulating a situation to get ahead at their expense. | Yes – You should feel their feelings because your actions have deeply affected their trust, self-esteem, and sense of security. |
| Miscommunication or Unclear Intentions (Moderate Responsibility) | When a misunderstanding or unclear communication causes hurt feelings, you may feel some level of responsibility, but it's not entirely your fault. | A text or email is misinterpreted because you didn’t express yourself clearly, leading the other person to feel hurt or confused. | Partially – You may feel their feelings, but this could also be a sign that better communication is needed in the future. |
| Honest Feedback or Setting Boundaries (Low Responsibility) | When you provide honest feedback or set boundaries, the other person may feel upset, but your responsibility is to prioritize your own well-being. | Telling a friend that their behavior is hurtful or saying no to a request because you need time for yourself. | No – While it’s okay to empathize with their feelings, you are not responsible for how they feel when you’re being honest or setting healthy boundaries. |
| Projected Emotions (No Responsibility) | When someone projects their emotions or insecurities onto you, you are not responsible for carrying their emotional weight, as it stems from their own inner struggles. | A colleague accuses you of being “unsupportive” even though you’ve been offering help, simply because they’re feeling stressed and overwhelmed. | No – You are not responsible for their emotions. Their feelings are projections based on their own experiences and not directly related to your actions. |
| Empathy Without Responsibility (No Responsibility) | When someone is upset, you can feel empathy for them, but you are not responsible for carrying their feelings. You can offer support without taking on their emotional burden. | Listening to a friend vent about a tough situation without internalizing their feelings or carrying their distress as your own. | No – While it’s okay to feel for them, you are not responsible for their emotions or their ability to process them. |